So, you’re wondering about the difference between HMO and PPO health insurance? Well, you’ve come to the right place! Health insurance can be a complex topic, but understanding the distinctions between different types of plans is essential for making informed decisions about your healthcare coverage. In this article, we’ll dive into the world of HMOs and PPOs, unraveling their unique features and helping you determine which one might be the best fit for you and your needs.
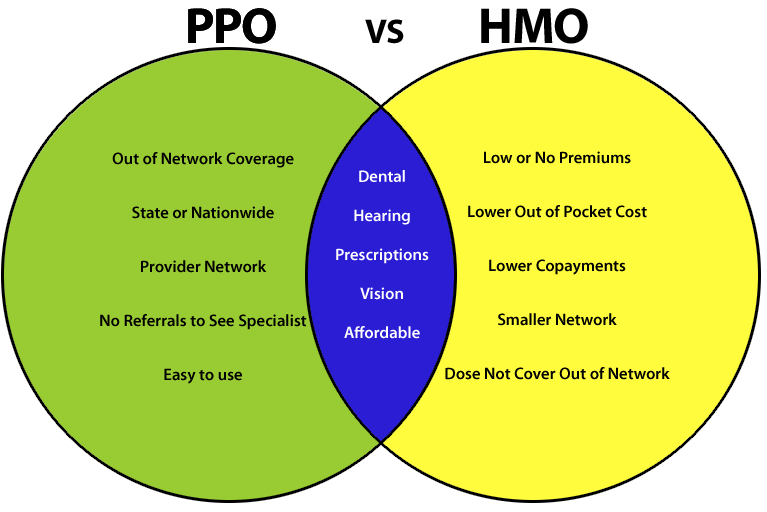
Regarding HMOs and PPOs, it’s like comparing apples and oranges – they may both be fruits but have distinct flavors. HMO stands for Health Maintenance Organization and operates on the principle of a tightly-knit network of healthcare providers. With an HMO plan, you’ll have a primary care physician (PCP) who will coordinate your healthcare needs. This means you’ll need a referral from your PCP to see a specialist. On the other hand, PPO stands for Preferred Provider Organization, and it offers a bit more flexibility. With a PPO plan, you can see any doctor or specialist without a referral. However, the catch is that staying within the network of preferred providers will save you more money in terms of co-pays and deductibles. Now that we’ve scratched the surface, let’s delve deeper into the differences between these two health insurance plans.
What is the difference between HMO and PPO health insurance?
Regarding health insurance, it’s essential to understand the difference between HMO and PPO plans. HMO, or Health Maintenance Organization, typically offers lower costs and requires you to choose a primary care physician for referrals. PPO, or Preferred Provider Organization, gives you more flexibility in choosing doctors and specialists but may incur higher costs. Ultimately, the choice between HMO and PPO depends on your healthcare needs and preferences.
Understanding the Difference Between HMO and PPO Health Insurance
Health insurance is essential to our lives, providing us with the financial coverage we need for medical expenses. Regarding health insurance plans, two common types are Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) and Preferred Provider Organization (PPO). While both offer coverage for medical services, they differ in flexibility, cost, and provider networks. Understanding the differences between HMO and PPO health insurance can help you make an informed decision when choosing a plan that best suits your needs.
The Basics of HMO Health Insurance
HMO health insurance plans typically have lower monthly premiums compared to PPO plans. This is because HMOs focus on providing healthcare services through a network of doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers. When you enroll in an HMO plan, you must choose a primary care physician (PCP) who will manage your healthcare needs. Your PCP will be a gateway to accessing specialists and other healthcare services within the HMO network.
One of the primary advantages of HMO health insurance is the emphasis on preventive care. HMOs often cover preventive services like annual check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings at little to no cost. Additionally, HMOs generally have lower out-of-pocket expenses, such as deductibles and co-pays, for in-network services. However, HMO plans typically require referrals from your PCP to see specialists and out-of-network services are not covered except in emergencies.
Benefits of HMO Health Insurance
1. Lower monthly premiums: HMO plans often have lower monthly premiums than PPO plans, making them more affordable for individuals and families.
2. Emphasis on preventive care: HMOs prioritize preventive services, ensuring that you receive regular check-ups and screenings to catch potential health issues early.
3. Lower out-of-pocket costs: In-network services typically have lower deductibles and co-pays, making healthcare more affordable for HMO members.
4. Coordinated care: With a primary care physician managing your healthcare needs, you benefit from coordinated care and a more personalized approach to your health.
Considerations for HMO Health Insurance
1. Limited provider network: HMO plans restrict you to a network of doctors and hospitals. An HMO plan may not be the best fit if you prefer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
2. Referrals required: Seeing a specialist typically requires a referral from your PCP, which can add an extra step to accessing specialized care.
3. Out-of-network services not covered: With HMO plans, non-emergency out-of-network services are generally not covered, so staying within the network for optimal coverage is essential.
The Basics of PPO Health Insurance
PPO health insurance plans offer a greater level of flexibility compared to HMO plans. With a PPO plan, you have the freedom to see any healthcare provider you choose, whether they are in-network or out-of-network. This means you can see a specialist without needing a referral from a primary care physician. However, staying within the PPO network often results in lower out-of-pocket costs.
PPO plans generally have higher monthly premiums than HMO plans, as they offer more flexibility and choice. They also have higher deductibles and co-pays for both in-network and out-of-network services. With a PPO plan, you can seek care from specialists or healthcare facilities outside the network, but you will likely pay more for these services.
Benefits of PPO Health Insurance
1. Greater provider choice: PPO plans allow you to see any healthcare provider you choose, giving you more flexibility and control over your healthcare decisions.
2. No referrals required: Unlike HMO plans, PPO plans do not require referrals from a primary care physician to see specialists.
3. Out-of-network coverage: PPO plans provide coverage for out-of-network services at a higher cost. This can be beneficial if you have a preferred specialist or healthcare facility outside the network.
4. Flexibility for travel: PPO plans offer coverage when you are traveling, including out-of-network benefits.
Considerations for PPO Health Insurance
1. Higher monthly premiums: PPO plans often come with higher monthly premiums than HMO plans, making them more expensive.
2. Higher out-of-pocket costs: PPO plans generally have higher deductibles and co-pays for both in-network and out-of-network services, resulting in higher out-of-pocket costs.
3. Balancing costs: While PPO plans offer flexibility, utilizing out-of-network providers can lead to higher costs, so weighing the benefits against the expenses is essential.
Choosing Between HMO and PPO Health Insurance
When deciding between HMO and PPO health insurance, it’s essential to consider your healthcare needs, budget, and preferences. Here are a few factors to consider:
1. Provider choice: If you have specific doctors or specialists you prefer to see, a PPO plan may be more suitable as it allows you to see providers outside the network.
2. Budget: An HMO plan may be a better fit if you are looking for lower monthly premiums and predictable out-of-pocket costs.
3. Referrals and coordination: If you prefer a more coordinated approach to your healthcare and don’t mind obtaining referrals, an HMO plan may provide the necessary structure.
4. Flexibility and travel: If you frequently travel or require specialized care outside of the network, a PPO plan offers the flexibility you need.
It’s important to carefully review the details of each plan, including the network of providers, coverage limitations, and costs, to determine which type of health insurance will best meet your individual needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between HMO and PPO health insurance is crucial when selecting a plan that aligns with your healthcare needs and preferences. HMO plans offer lower costs and a more structured approach to care, while PPO plans provide greater flexibility and choice. By considering factors such as provider networks, costs, and coordination of care, you can make an informed decision that ensures you have the coverage you need for your health and well-being.
Key Takeaways: What is the Difference Between HMO and PPO Health Insurance?
- HMO is a Health Maintenance Organization, while PPO is a Preferred Provider Organization.
- HMO plans require you to choose a primary care physician and get referrals for specialists, whereas PPO plans allow you to visit any healthcare provider without a referral.
- HMO plans generally have lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs, but PPO plans offer more flexibility and choice to healthcare providers.
- In HMO plans, you usually need to stay within a network of providers, while PPO plans allow you to visit out-of-network providers at a higher cost.
- When deciding between HMO and PPO health insurance, consider your healthcare needs, preferred providers, and budget to make the best choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an HMO health insurance?
An HMO, or Health Maintenance Organization, is a type of health insurance plan that typically requires you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who will coordinate your healthcare services. With an HMO, you generally need a referral from your PCP to see a specialist. HMO plans also usually have a network of healthcare providers you must use to receive the maximum benefits from your insurance.
While HMOs generally have lower out-of-pocket costs and premiums than other plans, they can be more restrictive regarding provider choice and require more paperwork for referrals and authorizations.
What is a PPO health insurance?
A PPO, or Preferred Provider Organization, is a type of health insurance plan that offers more flexibility regarding provider choice. With a PPO, you can see any healthcare provider you choose, both in and out of the network, without needing a referral from a primary care physician.
PPO plans typically have higher out-of-pocket costs and premiums than HMOs but offer more freedom in selecting healthcare providers. In-network providers usually provide discounted rates, while out-of-network providers may incur higher costs for the insured individual.
What are the main differences between HMO and PPO health insurance?
The main differences between HMO and PPO health insurance plans are the level of provider choice and the need for referrals. HMOs require you to choose a primary care physician to manage your healthcare and provide referrals for specialist care. PPOs, on the other hand, allow you to see any healthcare provider without needing a referral.
HMOs often have lower out-of-pocket costs and premiums, but they may have more restrictions on provider choice and require more referral paperwork. PPOs offer more flexibility regarding provider choice but generally have higher costs. When deciding between HMO and PPO health insurance, it’s essential to consider your healthcare needs, preferred providers, and budget.
Which type of health insurance is better, HMO or PPO?
The choice between HMO and PPO health insurance depends on your preferences and healthcare needs. If you prefer more control over your healthcare decisions and want the flexibility to see any provider without needing a referral, a PPO plan may be better for you. However, an HMO plan may be more suitable if you’re looking for lower out-of-pocket costs and don’t mind having a primary care physician manage your healthcare and provide referrals.
Consider factors such as your preferred healthcare providers, the level of coverage you need, and your budget when deciding between HMO and PPO health insurance. It’s also a good idea to review the network of providers for each plan to ensure your preferred healthcare professionals are included.
Can I switch from an HMO to a PPO or vice versa?
Generally, you can switch from an HMO to a PPO or vice versa during specific enrollment periods, such as during the annual open enrollment period or when experiencing a qualifying life event. However, you must check with your health insurance provider or employer to understand the rules and guidelines for switching plans.
Keep in mind that switching plans may impact your coverage and provider network, so it’s important to carefully review the new plan’s details before making any changes. Switching plans may also affect your premiums and out-of-pocket costs, so it’s essential to consider all factors before deciding.
Final Summary: The Difference Between HMO and PPO Health Insurance
After exploring the intricacies of HMO and PPO health insurance plans, it is clear that these two options differ in several key aspects. While HMO plans provide a more restricted network of healthcare providers and require referrals for specialist visits, PPO plans offer greater flexibility and allow individuals to see any doctor without referrals. Additionally, HMO plans tend to have lower monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs, making them more budget-friendly for those prioritizing cost savings. On the other hand, PPO plans typically have higher monthly premiums and allow individuals to see out-of-network providers at a higher cost.
Understanding the differences between HMO and PPO health insurance plans is essential in making an informed decision about the best option for you and your family. Whether you prefer the affordability and simplicity of an HMO plan or the flexibility and broader network of a PPO plan, it’s essential to consider your healthcare needs, budget, and personal preferences. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select the health insurance plan that aligns with your specific requirements and provides the coverage you need for a healthy and secure future. So, take the time to research and compare the options available to you, and make a choice that fits your unique circumstances.